Hosted Outshift Agent Directory, powered by AGNTCY
A public hosted instance of the Agent Directory is available at https://agent-directory.outshift.com/. In this section we describe the main features of this instance which is provided AS IS to the community to help users familiarize themselves with the Agent Directory.
Outshift Agent Directory (aka "Hub") is designed to provide a robust multi-organization platform for hosting and managing Agent Directory Records, which we will refer to as simply "records" or "agent records." Outshift Agent Directory acts as a centralized point for organizing and accessing agent records. This hosted service is enhanced by a gRPC API that supports efficient service communication and integration, ensuring seamless interaction between components.
Outshift Agent Directory serves as a central platform for hosting and managing various agent-related services. The main purpose of the Agent Directory Service component is to provide a comprehensive solution for developers and IT admins to register, discover, and manage records in an organized manner. By offering a secure environment for authentication and user management, it ensures that organizations can confidently manage their agent directories and related services.
Core Concepts
The Outshift Agent Directory is organized around a few basic concepts:
- Users - A user is the basic unit of authentication and authorization in the Hub, usually corresponding to a human or service account.
- Organization - An organization provides a way to group users for sharing agents and handling administrative tasks. A user can belong to many organizations, but organizations are flat and cannot belong to one another.
- Agent Records - An Agent Record is a collection of data and metadata about a particular agentic application or service. The schema of the Record is defined in OASF and contains, for example, a collection of skills. A record pushed to the Hub is added to only one organization, but the same record can be added separately to multiple organizations.
The Agent Directory Service (ADS) provides storage for agent records while the frontend hosted Outshift Agent Directory provides access control with Users and their Organizations and management of agent records in their organizations.
Features
Outshift Agent Directory, powered by AGNTCY, enables users to:
- View and search for public agent, A2A card, or MCP server records.
- View your organization's public and private agent, A2A card, or MCP server records.
- Publish agent, A2A card, or MCP server records to an organization.
- Access multiple separate organizations.
- Invite other users to your organizations.
Using the Hub
Signing up for the hosted Outshift Agent Directory and Logging in
To get started with the hosted Outshift Agent Directory, sign up for free at the Outshift Agent Directory homepage. You can sign up with your GitHub account or by providing an email and password. Once your account is created, simply log in. When first logging in, you are prompted to create a name for your default organization. This organization is a personal space where all records belong to you.
View and Search for Agents
The Explore page allows users to browse and search through available public agent records. It shows records from any organization that are set to public visibility.
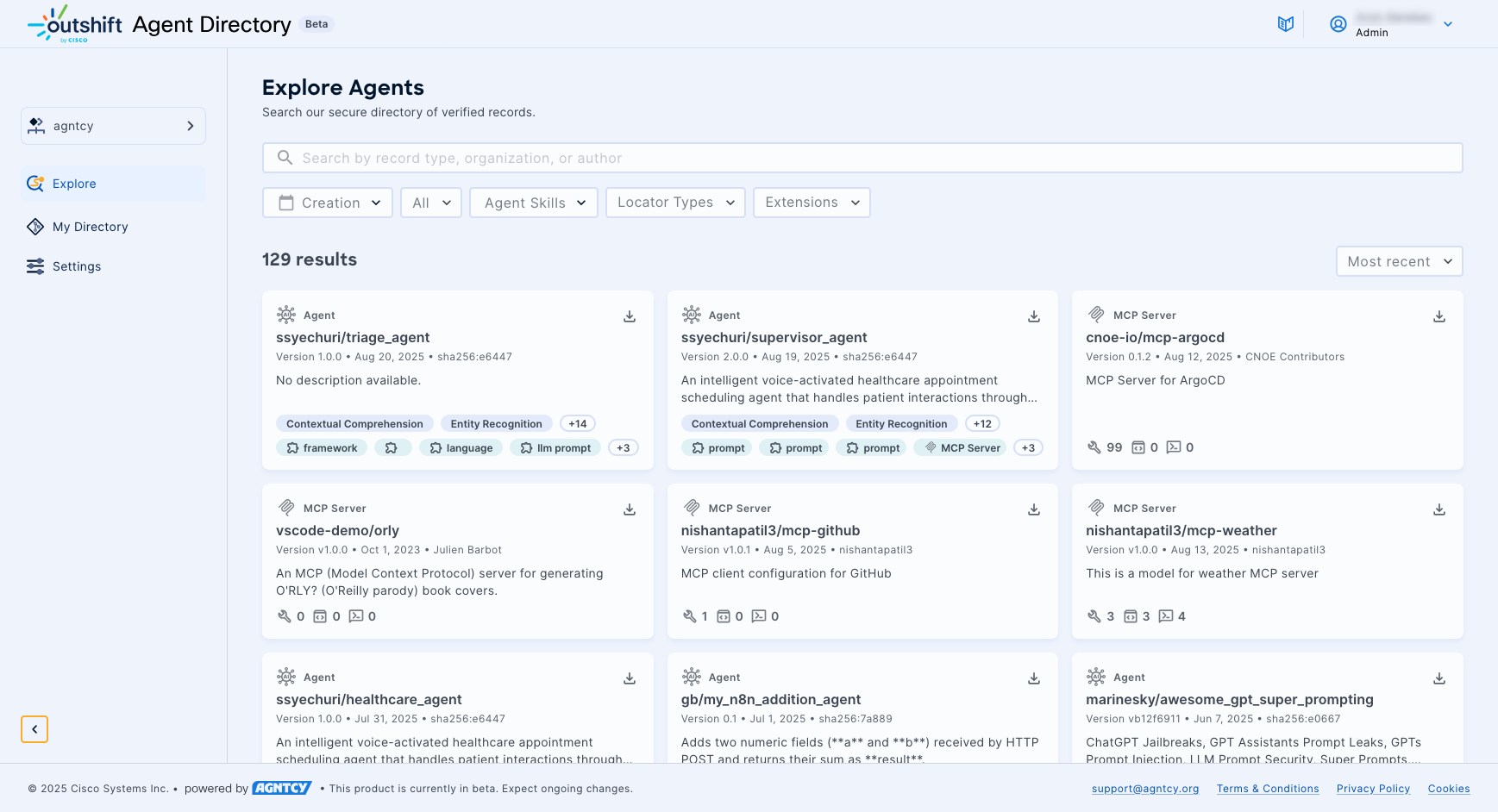
You can refine the results using predefined filters and open search:
- Use the Search bar to search for a text string in an agent record name. To clear the search bar, click the ×.
- Use the Creation filter to narrow the results by the date of creation of the record.
- Use the record type drop down menu to filter by agent or MCP server records.
- Use the drop-down Agent Skills list to narrow the results by skill.
- Use the drop-down Locator Types list to narrow the results by locator type.
- Use the drop-down Modules list to narrow the results by module name.
- Use the drop-down sort by list to sort the displayed items by most recent or oldest.
Manage Records Associated with Your Organization
The My Directory Page allows you to manage and view an organization's agent, A2A card, or MCP server records in the Outshift Agent Directory. Here the records are displayed in a table.
You can refine the results using predefined filters and open search:
- Use the Search bar to search for a text string in an agent record name. To clear the search bar, click the ×.
- Use the Creation filter to narrow the results by the date of creation of the record.
- Use the record type drop down menu to filter by agent or MCP server records.
- Use the drop-down Agent Skills list to narrow the results by skill.
- Use the drop-down Locator Types list to narrow the results by locator type.
- Use the drop-down Modules list to narrow the results by module name.
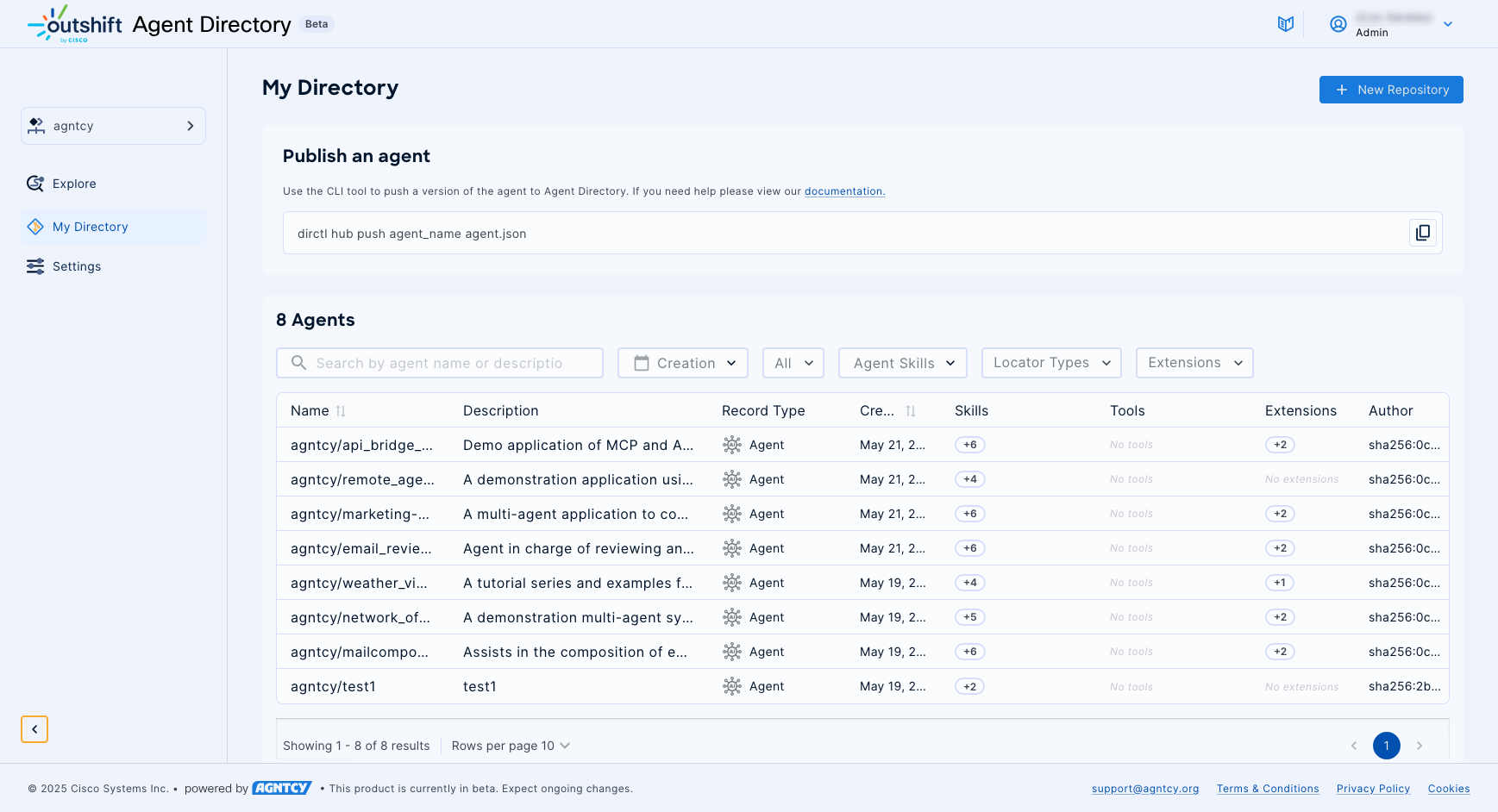
Agent Actions
Clicking the three dots (⁝) at the end of any row in the Agent Directory table opens a drop-down list of actions you can perform on that record.
- Click Edit agent to edit the record.
- Click Delete agent to remove the record from the directory, including all of its agent records.
Record Details
Clicking on an agent, A2A card, or MCP server opens the Record Details page with further information on the record.
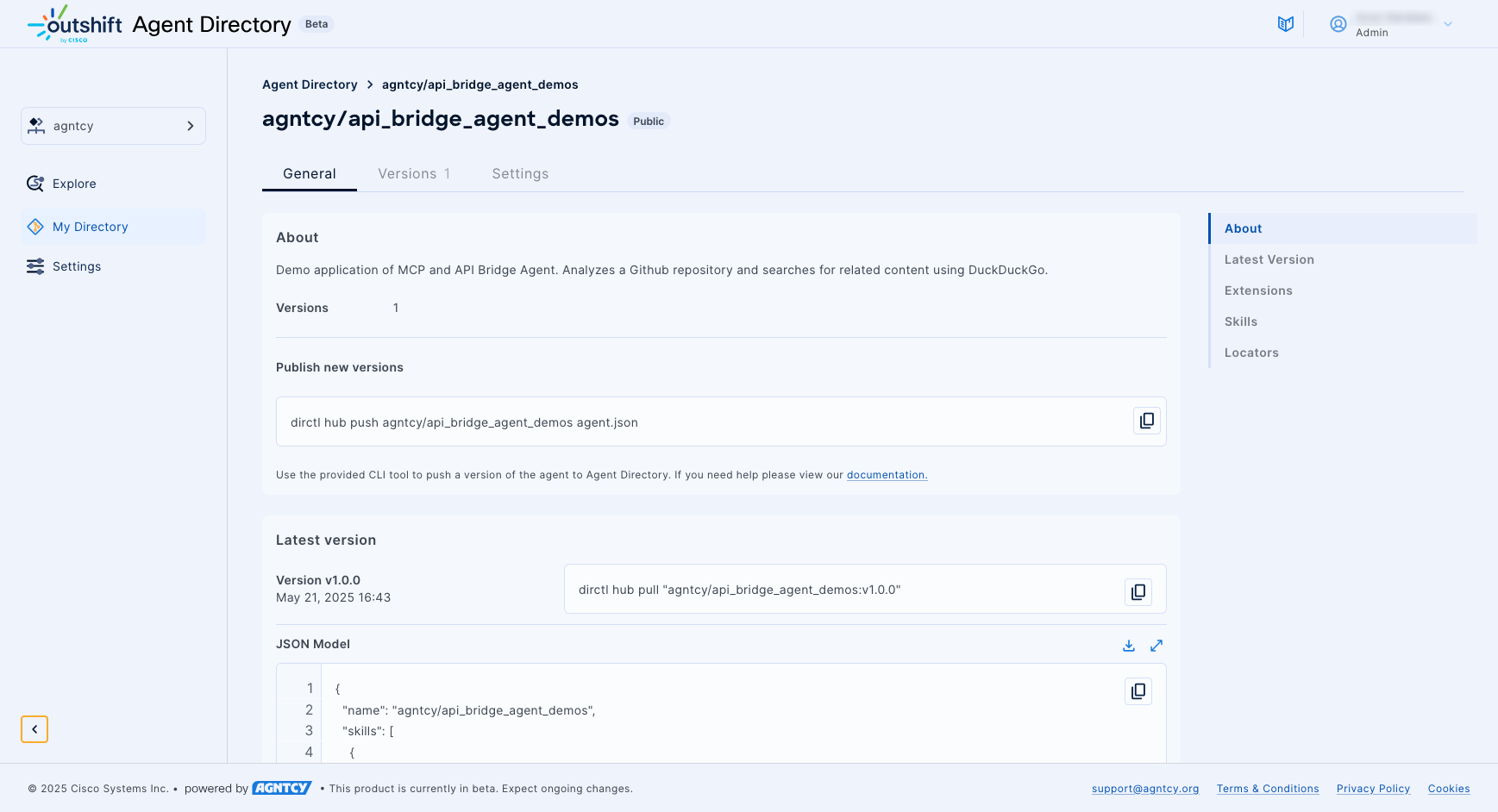
The General tab lists the following information from the record:
- A description and the creator of the record.
- The version number and date of publishing.
- The extensions of the record.
- For agent records:
- The skills associated with the agent.
- The locators of the agent.
- For MCP server records:
- The tools of the MCP server.
- The resources of the MCP server.
- The prompts of the MCP server.
The Related Versions tab lists the related versions of the record. Records are grouped using
the previous_record_cid OASF property in the agent record as the relation.
The Settings tab allows the owner to change the visibility of the agent.
Add an Agent Directory Record to the Outshift Agent Directory
Agent directory records are associated with an organization. An organization must exist first for an agent record to be added to it as described below: Create an Organization.
Adding an Agent Directory Record to an Organization
Adding an Agent Directory Record has the following prerequisites:
- The Outshift Agent Directory command line tool,
dirctl. - A signed agent record that conforms to Outshift Agent Directory requirements.
Installing dirctl
Binary packages and installation of the Outshift Agent Directory dirctl
command line tool are available in multiple forms on GitHub:
After installation, use the dirctl and dirctl hub commands to list the available commands.
Authenticating to the Outshift Agent Directory through dirctl
The dirctl command line tools supports two methods to authenticate to a Outshift Agent Directory account:
-
Interactive login
Interactive login is a web-based user authentication initiated from
dirctlas follows:$ dirctl hub loginThe login page opens in the browser allowing the user to enter their credentials.
-
API key based login
This is a programmatic way to authenticate via API key credentials:
-
Once logged in through interactive login, use the
dirctl hub apikey createcommand to generate the API key credentials, i.e. aclient_idand asecret, for a specific organization and with a specific role. One can store the client_id and secret as environment variables or as JSON file:$ dirctl hub apikey create --org-name your-user --role ROLE_ADMIN DIRCTL_CLIENT_ID=3603e7f1-6903-44ec-868e-b78fab3cf43f@ak.eticloud.io DIRCTL_CLIENT_SECRET=*********************************************$ dirctl hub apikey create --org-name your-user --role ROLE_ADMIN --output json > api-key-creds.json -
Set the environment variable and use the dirctl commands as usual or provide the JSON file with the credentials:
$ dirctl hub [command] --apikey-file api-key-creds.json -
For more details
dirctl hub apikey --helpNote
Interactive authentication using
dirctl hub logintakes precedence over API key subcommands. If you want to ensure that you are using the API key for authentication, log out withdirctl hub logout.Note
In Release v0.3.0, API key support is enabled for dirctl hub push and pull operations only.
-
Creating an Agent Directory Record
An Agent Directory record is stored in JSON format. The record is specific to one entry in the Agent Directory, though the same record can be added to multiple organizations. The structure of each AD record is defined by the OASF starting at the root with an Agent object.
To be useful, an agent, A2A card, or MCP server record should include at least the following:
- Name of the agent, A2A card, or MCP server.
- Version of the agent, A2A card, or MCP server (use semantic convention).
- Description: something to help any viewer understand what your agent, A2A card, or MCP server does, what is the use case it is applicable to, expected inputs and outputs, LLM used, runtime, etc.
- Locator, per OASF locator objects.
- Types (source code, agent as a service, docker image, etc) matching the supported types in the OASF locator objects.
- URL (corresponding address to find the agent).
- Skills, following the OASF skills schema.
- Previous Record CID: if this is a new or related version to another record, indicate the CID of the related record.
And it will look like this:
{
"schema_version": "0.7.0",
"name": "my-agent",
"version": "2.0",
"authors": [
"Organization Name"
],
"description": "This agent takes any text input and condenses it down to 3 bullets of less than 100 characters each using any LLM.",
"created_at": "2025-08-11T16:20:37.159072Z",
"locators": [
{
"url": "https://github.com/example/agent_A",
"type": "source_code"
}
],
"skills": [
{
"id": 10201,
"name": "natural_language_processing/natural_language_generation/text_completion"
}
]
}
Using the Record Composer
As an alternative to manually creating JSON files, the Outshift Agent Directory provides a web-based Record Composer that simplifies the creation of Agent Directory Records through a guided interface. This tool streamlines the record creation process while ensuring compliance with OASF schema requirements.
The Record Composer offers the following features:
- Guided forms with real-time validation.
- Import capabilities to document existing configurations.
- Seamless integration with the Hub's organizational structure.
Accessing the Record Composer
To access the Record Composer, log into your Outshift Agent Directory account at https://agent-directory.outshift.com/ and click Record Composer in the left navigation menu. The interface provides immediate access to the record creation workflow within your organization's context.
Getting Started with Record Creation
The Record Composer offers two primary approaches to creating agent directory records. You can import existing A2A cards or MCP server configurations to quickly convert your current setups into OASF-compliant records. Alternatively, you can start from scratch to build records with complete control over all fields and configurations.
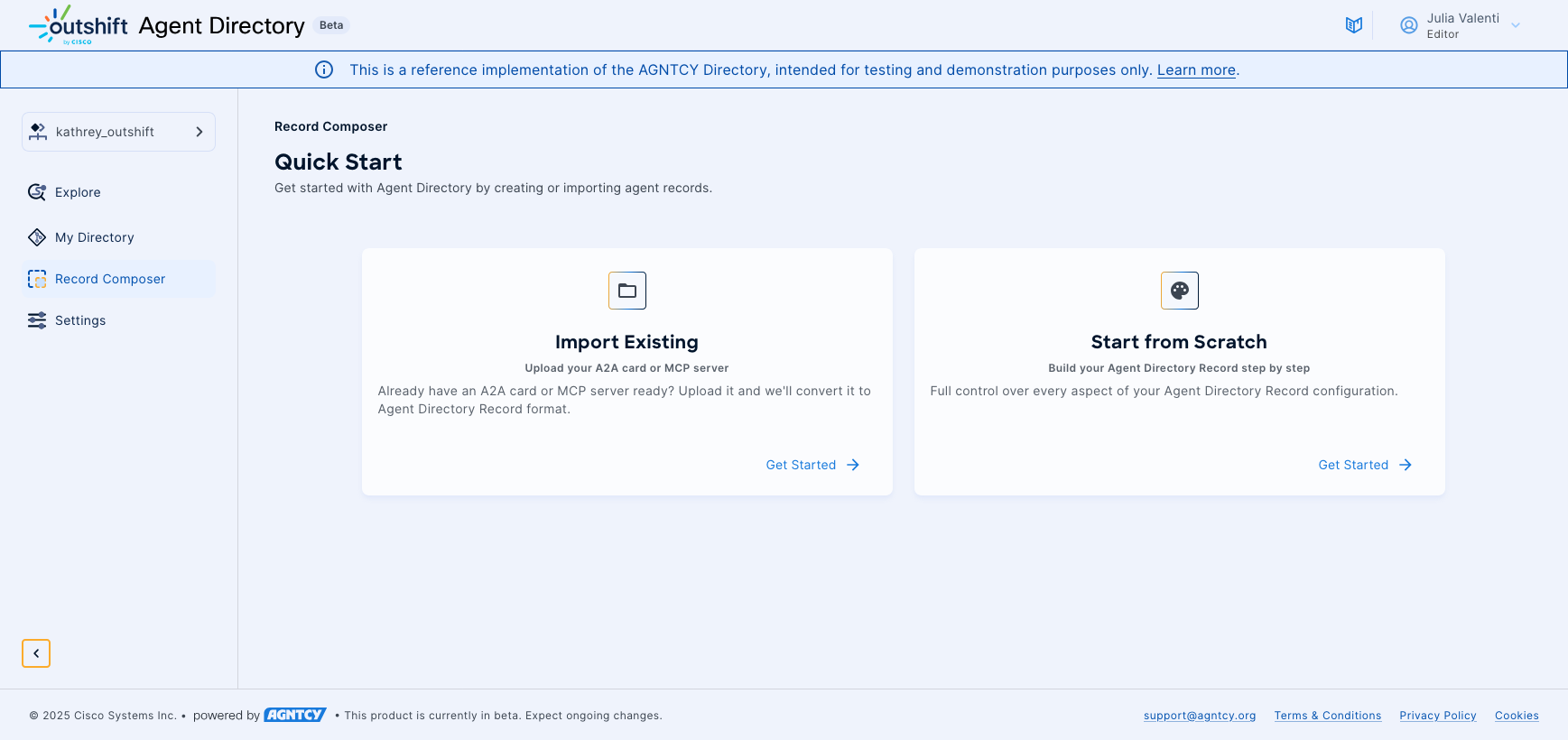
Configuring Record Metadata
Every agent directory record requires fundamental metadata that integrates seamlessly with your Hub organization. The composer automatically pre-populates author information from your Hub profile.
You need to provide the following details:
- A unique name for your agent.
- A comprehensive description that helps users understand the agent's purpose and capabilities.
- A semantic version following standard conventions.
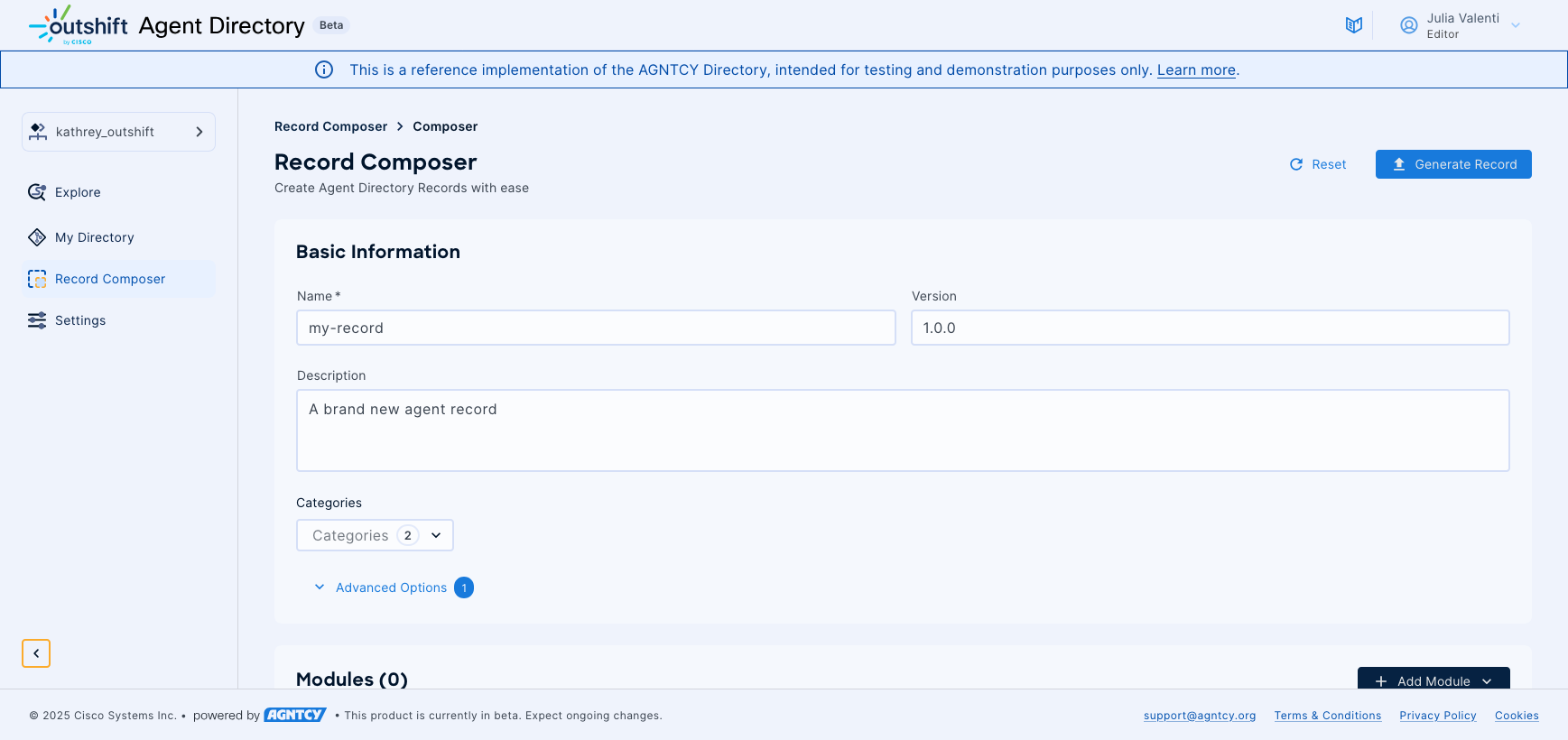
You can also provide skill classifications in-line with the OASF taxonomy. This skill classification aids in discoverability within the Hub's search functionality, helping users find agents with specific capabilities. Optional fields such as license information, searchable tags, and locator URLs following the OASF locator schema can be added to provide additional context and accessibility.
Adding Functional Modules
The modular architecture of OASF records allows you to document different types of agent capabilities through specialized module types. Each module represents a specific functional aspect of your agent or service that you want to communicate to directory users.
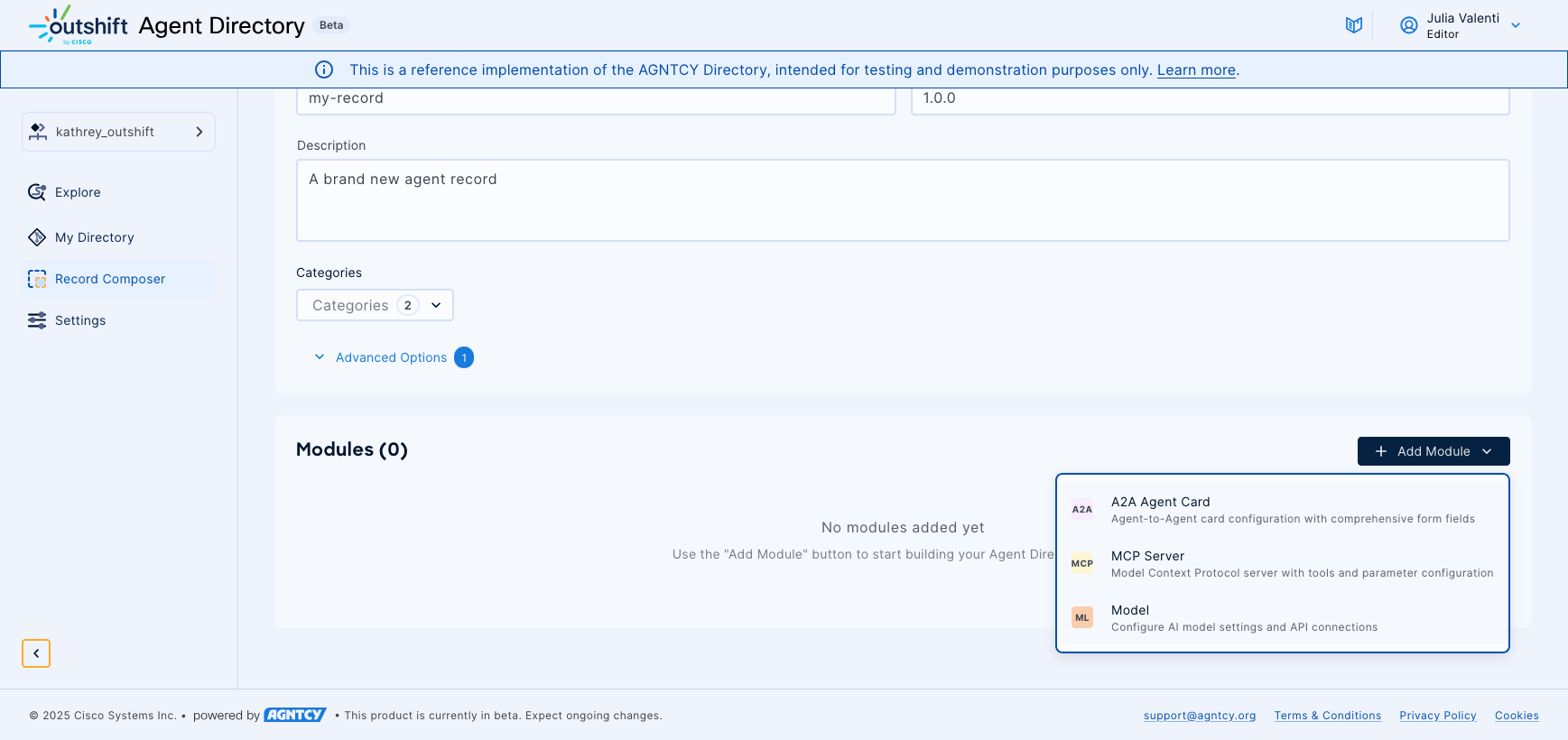
If your agent uses A2A (Agent-to-Agent), you can add A2A Agent Card modules to document and communicate the existence of your A2A capabilities to users browsing the directory.
These modules capture essential details about your agent:
- Endpoint URL.
- Supported protocol versions.
- Input and output handling modes.
- Specific capabilities such as streaming support or push notifications.
This documentation helps other developers understand what A2A features your agent supports.
MCP Server modules allow you to document the existence and capabilities of your Model Context Protocol server for directory users. These modules communicate server connection details across different transport methods including stdio, HTTP, and Server-Sent Events.
To inform potential integrators about your MCP server's capabilities, you can document available tool definitions:
- Parameter schemas.
- Prompt configurations with argument specifications.
- Resource metadata with access patterns.
Model Configuration modules enable you to document which AI models and providers your agent utilizes, helping users understand your agent's underlying capabilities. These modules communicate information about provider selection from supported services like OpenAI and Anthropic, model name and version specifications, API endpoint details, and generation parameters such as temperature and token limits that your agent employs.
Validation and Quality Assurance
The Record Composer implements comprehensive validation that operates in real-time as you build your record. This validation system ensures OASF schema compliance while checking against your organization's specific policies and existing record inventory.
The validation process includes schema compliance verification to ensure your record meets format specifications, organizational rule enforcement to maintain consistency within your Hub organization, and conflict detection that prevents duplicate name and version combinations within your organization. Additionally, the system validates URL accessibility for locator fields and ensures all required information is present for successful Hub publication.
Downloading and Publishing Records
Once your record passes validation, the composer generates an OASF-compliant JSON file ready for publication to the Hub. The interface provides clear instructions for the subsequent signing and publishing process using the dirctl command-line tool.
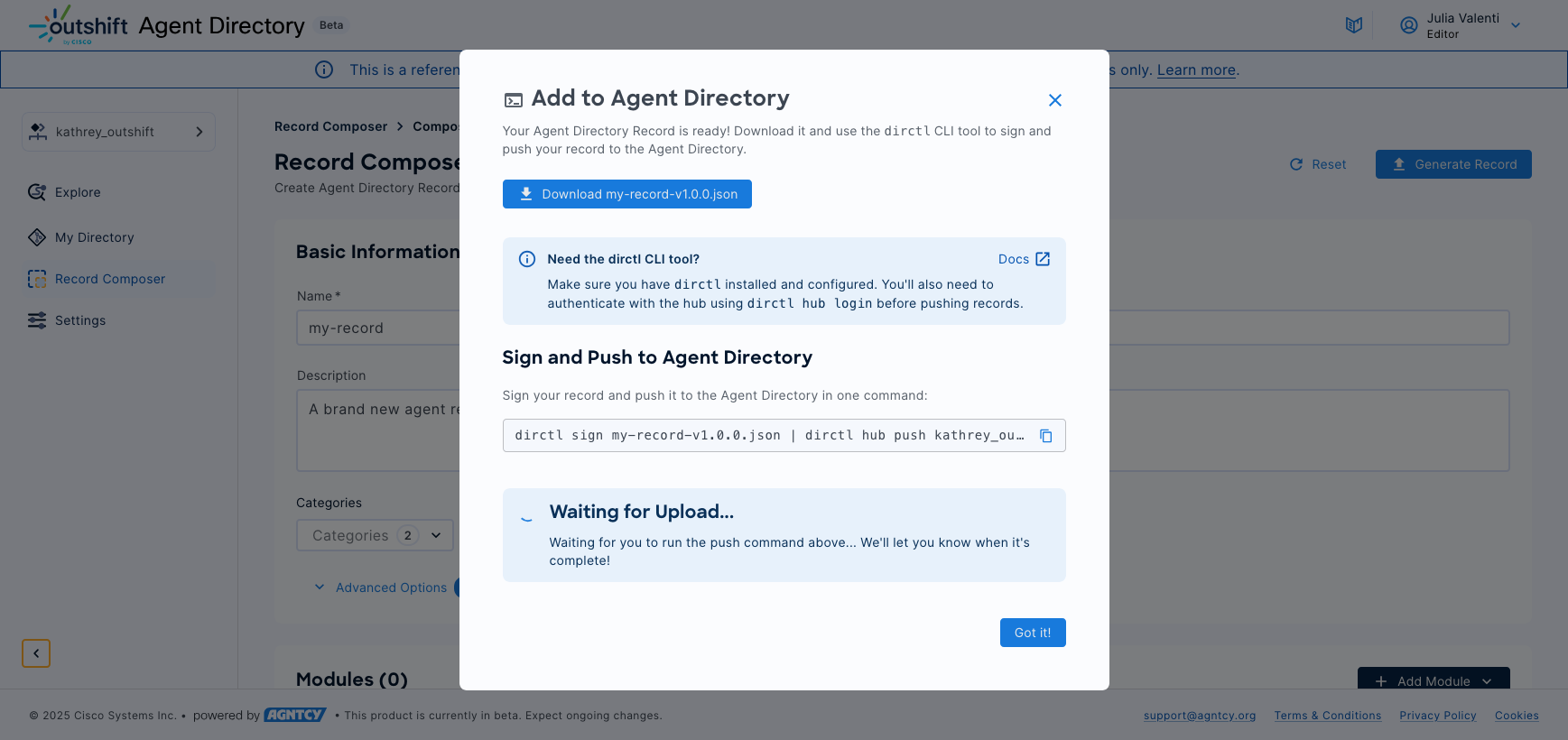
The generated file integrates seamlessly with the existing dirctl workflow, maintaining compatibility with the established signing and publishing procedures described in the following sections of this documentation.
Importing Existing Configurations
The Record Composer supports importing existing agent configurations to accelerate the record creation process and facilitate migration from other formats.
For A2A Agent Cards, you can upload JSON files directly from your .well-known/agent.json endpoint. The system automatically extracts agent capabilities, skills, and protocol versions, converting them into the appropriate OASF module format. This automated extraction significantly reduces manual data entry while ensuring accuracy in the conversion process.
MCP Server configurations can be imported through a structured multi-step process that handles the complexity of Model Context Protocol specifications. The import workflow guides you through documenting connection details for server transport, documenting available tools from tools/list endpoints, documenting prompt capabilities from prompts/list endpoints, and documenting resource information from resources/list endpoints. Each step supports both file upload and direct JSON input with comprehensive schema validation.
Pushing Agent Directory Records using dirctl
Once all prerequisites are met, you are ready to push an agent record to an organization that you have write access to.
Pushing and pulling Agent Directory records is done using the dirctl tool.
From your terminal window:
-
Authenticate to your Outshift Agent Directory account using one of the methods described above.
-
Push your conforming agent record to the desired organization:
dirctl hub push \ <organization> \ <record json>In case of API key authentication set the needed environment variables or provide the API key credential file:
dirctl hub push \ <organization> \ <record json> --apikey-file api-key-creds.jsonIn case of interactive login, when you're done, logout of your hub account
dirctl hub logout
Signing Agent Directory Records using dirctl
You should sign the record after pushing it to the Outshift Agent Directory.
To sign an agent, A2A card, or MCP server record using the default provider Sigstore, run:
dirctl hub sign <organization> <record CID>
You can find the CID of the record output from the push command or in the record details page in the Hub UI.
The signing service login page opens in your browser. Use your credentials to log in. The agent, A2A card, or MCP server record will be augmented with a generated signature.
You can validate the record using the OASF Schema API.
You can validate the signature(s) using:
dir hub verify <record CID>
For further details on signing, use the dirctl hub sign --help command.
Pulling Agent Directory Records using dirctl
You can also pull an Agent Directory record via dirctl using the command listed on the agent details page.
Verifying an Agent Directory Record Signature
The verification process allows validation of the agent record signature against a specific identity.
To verify that an agent record is properly signed, you can run dirctl
verify agent.json.
To verify the signature against a specific identity, for example to check if an agent record originates from GitHub AGNTCY users, run:
dirctl hub verify agent.json \
--oidc-issuer "(.*)github.com(.*)" \
--oidc-identity "(.*)@agntcy.com"
For further details on verification, please checkout dirctl hub verify --help
Managing Organizations and Users
Settings
The settings page allows you to manage your organizations and their users.
List Organizations
Organizations represent groups of users within the Hub, each with its own set of records. Users can be members of many organizations. The organizations available to you are listed under the Organizations tab
Create a new organization
To create a new organization:
- Click the + Create Organization button.
- Enter the organization name.
- Click the Create organization button.
- Click the Finish button.
Manage Users
The list of users of the current organization is accessible by clicking on the organization (in bold) in the list.
You can invite other users to the organization by clicking the + Invite User button.
Note
You cannot invite other users to your personal organization created during signing up. To collaborate with others, create a new organization and invite them to it.
Troubleshooting pushing agents to the Outshift Agent Directory
Error: failed to validate access token: invalid session token
You forgot to login to your Outshift Agent Directory account
Error: failed to push agent: could not receive response: rpc error: code = AlreadyExists desc = agent: data model with same version already exists
You are trying to upload a new agent record with the same name and version as one that exists already. Update the version number in the JSON file.
Details on other uses of the dirctl command to interact with the
Agent Directory are
available in the documentation.
After installation, use the dirctl hub command to list the available commands.